What are executive function skills for all?
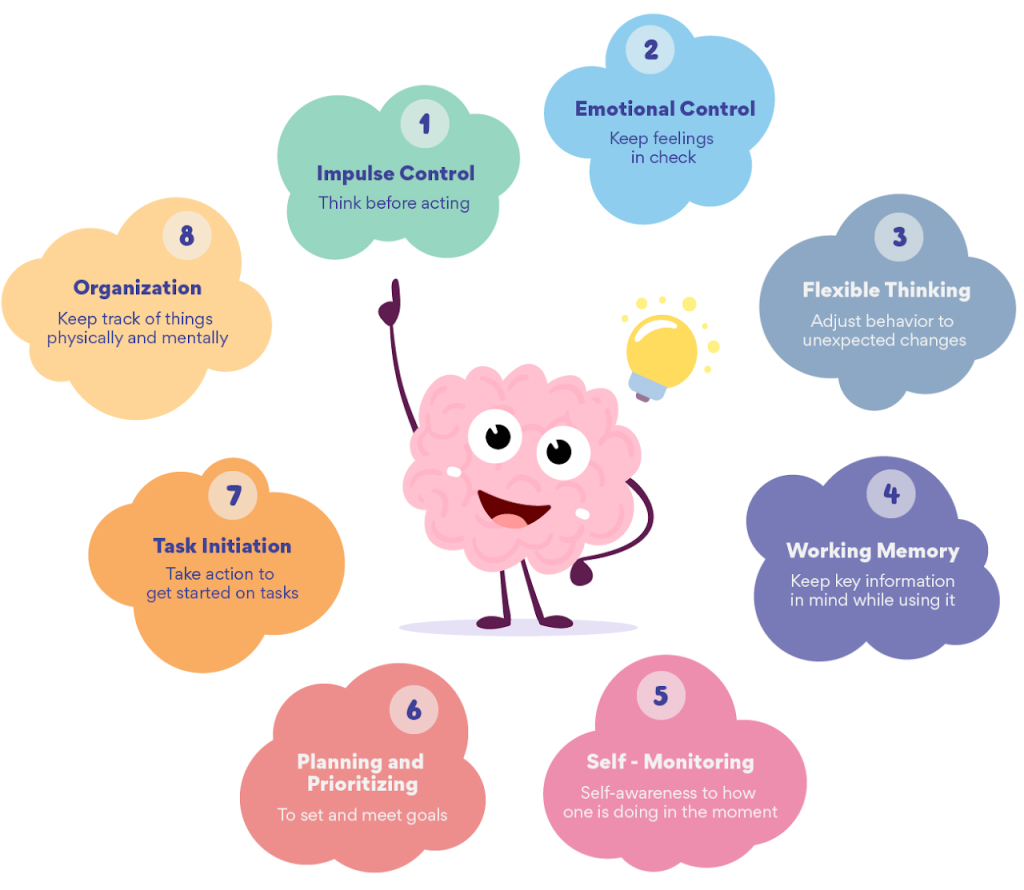
Executive functioning are the mental processes involved in planning, focusing attention, remembering instructions, and completing tasks. There is no agreed upon list but there are three main skills: working memory, inhibitory control, and cognitive flexibility. In order to successfully activate these functions, the brain develops these skills to filter distractions, prioritize tasks, set and achieve goals, and control impulses.



Working Memory
Also called short-term memory, working memory is limited, but it allows people to keep information in mind while using it.
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility, or flexible thinking, is the ability to adapt our thinking in response to an ever-changing environment.
Inhibitory-Control
Inhibitory control is a learner’s capacity to self regulate and be “in charge” of their thoughts and actions. Effective self control enables people to establish priorities and repel impulsive actions.
What does executive function skills for all look like in the classroom?
Support Working Memory
- Make instructions or expectations visible in the class.
- Combine images and words for instructions. Combined, this reduces demands placed on working memory.
Support Cognitive Flexibility
- Base the classroom experience on routines.
- Model flexible thinking both academically and socially.
- Teach a single concept or idea from more than one perspective.
- Ask students to solve problems in “another way.”
Support Self Control
- Intentionally incorporate movement, standing, and/or stretching into the lesson.
- Be explicit with what behaviors you wish to see.
- Remove unnecessary distractions from the classroom.
- Create purposeful breaks in class.
- Use a timer to set parameters around a learning experience or activity.
Resources
- Harvard Center for the Developing Child
- What is executive function? understood.org
- Helping Students Develop Executive Function Skills, Edutopia
- Using Games to Help Students Develop EF Skills, Edutopia
- Supporting EF Skills by Asking Questions, Edutopia
- Executive Functioning and Kindergarten Readiness, Edutopia

