Supporting
Dynamic Learners
An Introduction to
Dynamic Learning
Learning is complicated. There are many factors that allow you to learn. Everyone’s profile is unique and always changing given that no one brain is exactly the same and our brains are always changing. At any given moment we have current strengths as learners and current opportunities for growth depending on the content, task, and the learning environment. It’s for that reason that it’s essential that learners develop not only a knowledge of these current strengths and opportunities but also a “toolkit” of strategies that help learners leverage their strengths to help strengthen their opportunities for growth.
Here are some of the things that students need to know about neuroplasticity:
The more we use a skill, the stronger the neural pathways for that skill become. This is why retrieval practice is so important.
Stress can hinder neuroplasticity, so it is important to find ways to manage stress.

The concept of “current”
The concept of current is key to understanding learning as a dynamic process, reflecting a student’s state at any moment. Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and rewire in response to experiences, underpins lifelong learning. This adaptability explains how people can acquire new skills even later in life. Being a student means that factors like a friend’s glance can disrupt focus and memory, redirecting cognitive energy to process new social cues and not the content of class.
Deep Dives into Learning
Resources, tips and guidance to help all students thrive as learners
- All
- Deep Dives
- Sparking Conversations
- Parent Resources

Motivation
Expectancy, Value, and Cost Theory puts forth the argument that achievement related choices are motivated by a combination of 3 factors: expectancy, value, and cost.

Mindsets that Promote Resilience & Determination
The Student Experience Network has organized its research and content around three distinct learning mindsets. These mindsets foster learning.

Executive Function Skills for All
Executive functioning are the mental processes involved in planning, focusing attention, remembering instructions, and completing tasks.

Spaced Retrieval Practice
Spaced retrieval involves taking a given amount of time spent practicing skills, behaviors, or recalling information, and organizing that time into multiple sessions spread over the time.

The Role of Emotion in Learning
“The ability to feel passionate about something is a skill.” – Mary Helen Immordino-Yang

What Is Cognitive Load
Cognitive Load Theory is rooted in the idea that a human being’s working memory, or the short term memory required to complete an immediate task or operation, is limited.

Executive Function Skills for All
Executive functioning are the mental processes involved in planning, focusing attention, remembering instructions, and completing tasks.

What Is Cognitive Load
Cognitive Load Theory is rooted in the idea that a human being’s working memory, or the short term memory required to complete an immediate task or operation, is limited.

More on Metacognition
In basic terms, metacognition is when learners think about their thinking. Said another way, it is a person’s ability to self-critique how they approach a task

Metacognition
What is metacognition? Often explained as “thinking about your thinking,” metacognition is really about monitoring and controlling your thought processes.

Understanding Neuroplasticity
Understanding neuroplasticity helps us ask the right questions to encourage our children to develop a growth mindset.
There is no post

Motivation
Expectancy, Value, and Cost Theory puts forth the argument that achievement related choices are motivated by a combination of 3 factors: expectancy, value, and cost.

Mindsets that Promote Resilience & Determination
The Student Experience Network has organized its research and content around three distinct learning mindsets. These mindsets foster learning.

Spaced Retrieval Practice
Spaced retrieval involves taking a given amount of time spent practicing skills, behaviors, or recalling information, and organizing that time into multiple sessions spread over the time.

The Role of Emotion in Learning
“The ability to feel passionate about something is a skill.” – Mary Helen Immordino-Yang

Brain Basics
The brain is comprised of four main regions, each playing critical roles in learning.
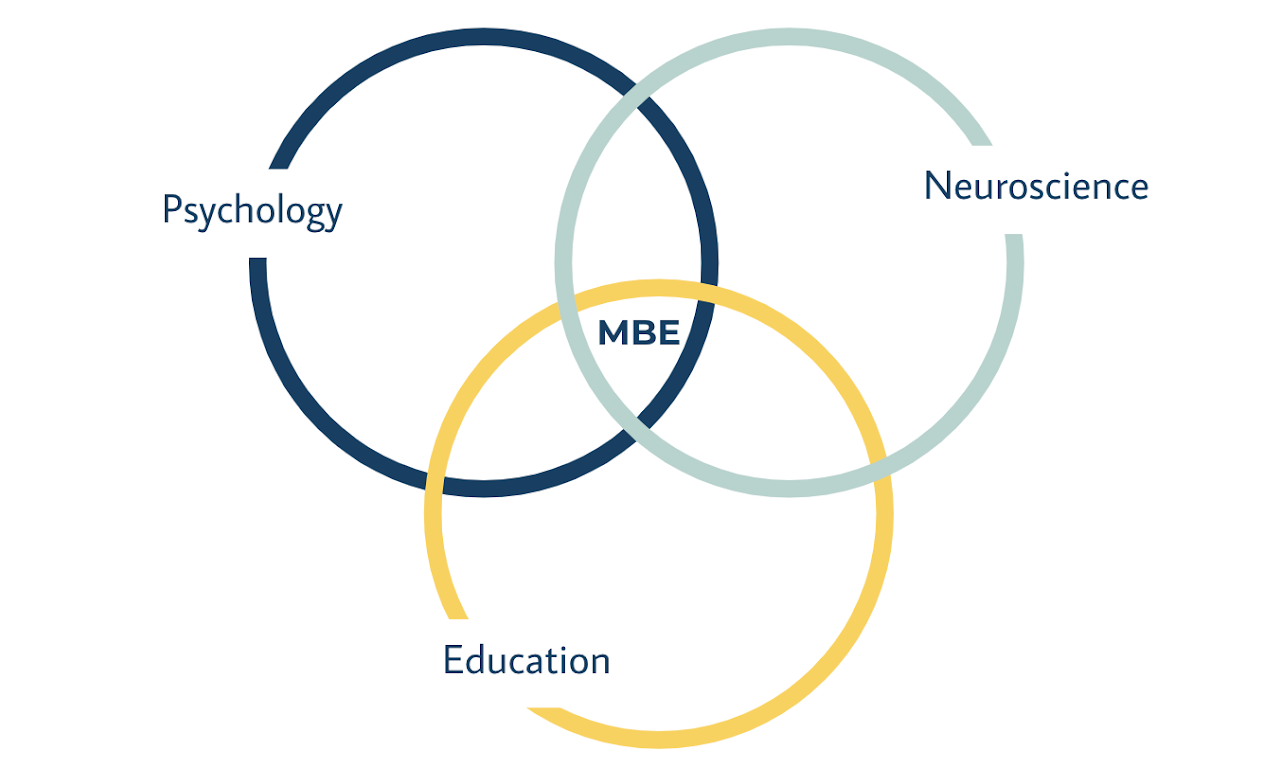
What is Mind, Brain, Education
The field of MBE began at Harvard University’s Graduate School of Education under the leadership of Dr. Kurt Fisher who saw the power of uniting the fields of neuroscience, psychology, and education.
